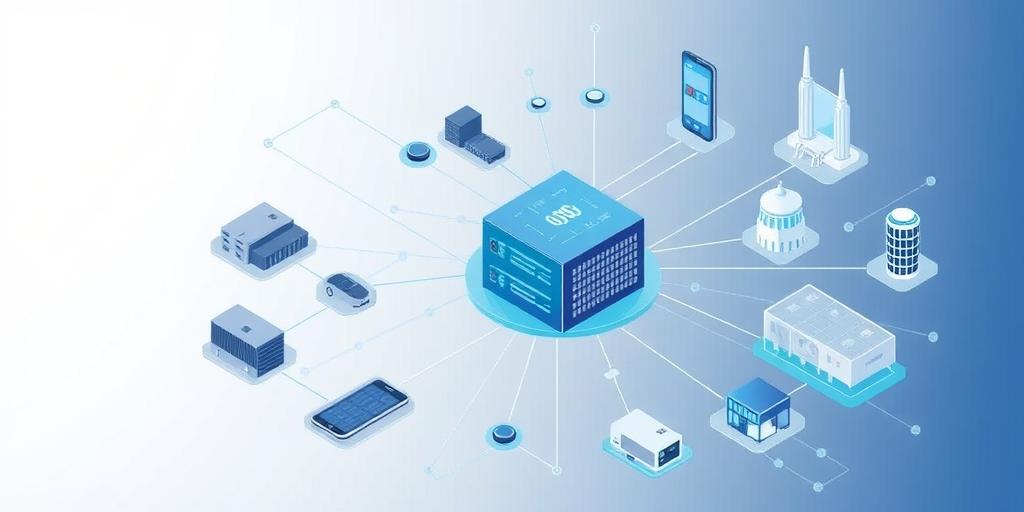
What is Edge Computing and Why Does It Matter?
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, edge computing has emerged as a transformative paradigm, reshaping how we process and utilize data. This article provides a comprehensive overview of edge computing, exploring its definition, key components, benefits, and diverse applications.
Defining Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings data processing closer to the source of data generation, or "the edge" of the network. Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data is transmitted to a centralized data center for processing, edge computing enables data to be processed locally, reducing latency, bandwidth consumption, and reliance on network connectivity.
Key Components of Edge Computing
The edge computing ecosystem comprises several essential components:
- Edge Devices: These are the devices that generate data at the edge of the network, such as sensors, actuators, smartphones, and industrial equipment.
- Edge Nodes: These are computing devices located closer to the edge devices than the central data center. Edge nodes can be servers, gateways, or even powerful embedded systems.
- Network Infrastructure: The network infrastructure connects edge devices to edge nodes and edge nodes to the central data center, facilitating data transmission and communication.
- Edge Computing Platform: This software layer provides the necessary tools and services to manage and orchestrate edge computing resources, including data processing, storage, and security.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers a wide range of benefits, making it an attractive solution for various applications:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing minimizes latency, enabling real-time decision-making and responsiveness.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Edge computing reduces the amount of data transmitted over the network, conserving bandwidth and lowering network costs.
- Enhanced Reliability: Edge computing enables applications to continue operating even when network connectivity is intermittent or unavailable.
- Improved Security: Processing data locally reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Scalability: Edge computing allows for the deployment of computing resources closer to users and devices, enabling greater scalability and flexibility.
Diverse Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing is transforming various industries and enabling new applications:
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing enables real-time monitoring and control of industrial equipment, improving efficiency and safety.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing provides the low latency and high bandwidth required for autonomous vehicles to make critical decisions in real-time.
- Healthcare: Edge computing facilitates remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and other healthcare applications, improving patient outcomes.
- Retail: Edge computing enables personalized shopping experiences, improved inventory management, and enhanced security in retail environments.
- Smart Cities: Edge computing supports various smart city applications, such as traffic management, public safety, and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a revolutionary technology that is transforming how we process and utilize data. By bringing data processing closer to the source, edge computing offers numerous benefits, including reduced latency, bandwidth optimization, enhanced reliability, improved security, and scalability. As edge computing technology continues to mature, it will play an increasingly important role in various industries and applications, enabling new possibilities and improving our lives.